Adjective
In linguistics, an adjective represents the features of a living being or a non-living being. So, in this article, we will learn about 7 types of adjectives, their meaning and examples.
What is an Adjective?
An adjective is a word that expresses the nature or qualities of a being (nouns or pronouns) in a sentence.
For example,
Sumit is a brave boy.
In the above example, we are talking about the quality of Sumit i.e. “brave“. So, here this quality is an adjective.
7 Types of Adjectives
We categorize the adjectives into 7 types:
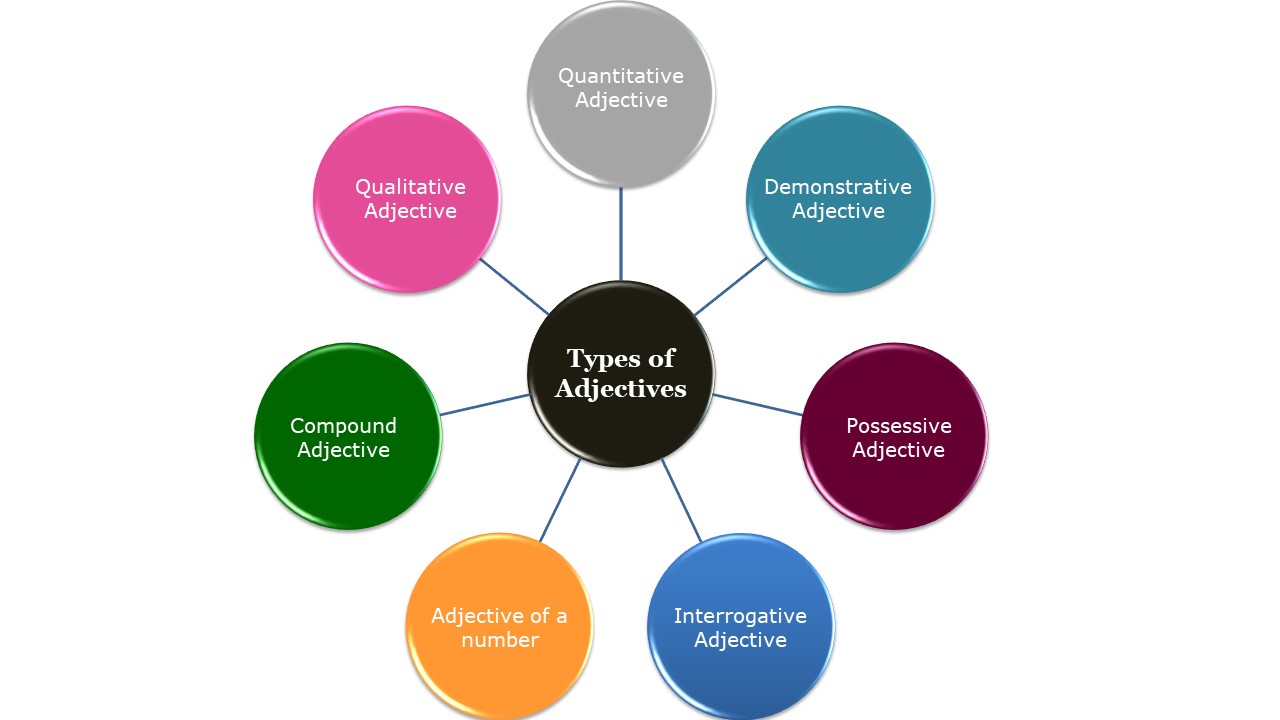
Now, we will learn more in detail about these 7 types of adjectives.
Qualitative Adjective
A word that reveals the quality or attributes of a noun or pronoun. Here, quality means the thing is good or bad, tall or short, sweet or bitter, large or small, etc.
For Example:
- I saw a beautiful idol of God in the temple.
In this example, the quality of the idol of God is “beautiful”. So, beautiful is a qualitative adjective.
- We eat a sour mango at the mango carnival.
In this example, the quality of the mango is “sour”. Thus, sour is a qualitative adjective.
- Premlata sleeps on a wrinkled couch.
In this example, the attribute of a couch is “wrinkled”. So, wrinkled is a qualitative adjective.
- He manufactured an economical gadget to save electricity.
In this example, the attribute of the gadget is “economical”. So, economical is a qualitative adjective.
- Rahul made a spicy pizza.
In the above example, the quality of the pizza is “spicy”. So, spicy is a qualitative adjective.
Quantitative Adjective
- A word that describes the quantity of a being, whether it is a noun or pronoun.
- We can also recognize the quantitative adjective by asking “How much” as it is used with an uncountable noun.
For Example:
- He didn’t have enough time to complete the project before the deadline.
- Tanya eats a whole bowl of salad.
- There isn’t much porridge left in the bowl.
- I guess more evidence needs to be discovered in this investigation.
- Rishi leaves some drops of oil on the floor.
Demonstrative Adjective
- A word referring to someone or something. The demonstrative adjectives are “This, That, These, and Those”.
- It always comes before nouns.
- We can say that demonstrative adjectives are words used to point out something about someone.
For Example:
- These cats are ferocious.
- This pot is deep.
- Those speakers were cheap.
- That bike is mine.
- That lawn is extensive.
Possessive Adjective
- Possessive adjective exhibits guardianship, or we can say belongingness of something to someone.
- Examples of possessive adjectives are – my, our, your, his, her, our, and their.
- So, the important thing is how to recognize the possessive adjective. So, firstly it always comes before the noun. And secondly, all possessive adjectives show the ownership of something.
For Example:
- My laptop needs to be fixed today.
- Our house lease is ending within a week.
- Your business is touching the heights of success.
- Her bicycle is in the garage.
- Their shop is always full of customers.
Interrogative Adjective
- An interrogative adjective enquires about something through a question.
- The interrogative adjectives are only 3W – What, Which, and Whose.
- These words will not be viewed as adjectives if they are not followed by nouns just next to them.
For Example:
- What name would you suggest for the baby?
- Which flower is a hybrid in this garden?
- Whose musical play do you love?
- Which bike is the most expensive one in this showroom?
- Whose doorbell did you ring?
Adjective of a number
- Adjective of a number shows the number and order of a person or thing.
- It shows “How many” things or persons are being explained.
For Example:
- There are still two vacancies for accountants in my company.
- This is the fifth bouquet I received today.
- Today I have only two meals in a whole day.
- We showcased four projects in a school.
Adjective of a number are divided into 3 types:
i) Definite Numeral Adjectives
Definite Numeral Adjective states specific numerals, position, and ranking.
It includes two, fifteen, triple, quarter, one-sixth, twenty-fifth, sixth, first, etc.
Definite numeral adjectives are categorized into two types:
a) Cardinal
Cardinal represents numbers or we can say digits.
Examples: one, five, fifty, twenty-five, ninety, hundred, sixty-three, and so on.
For Example:
- We watch three movies yesterday.
- Mishka wins four gift hampers from a supermarket bonanza offer.
- I poured the apple juice into ten glasses.
- My father gave me a hundred rupees on my birthday.
- I saw two squirrels eating bread crumbs.
b) Ordinal
Ordinal represents the ordering or position of the nouns. So, the ordinals are fifth, sixth, tenth, thirteenth, fifteenth, fourth, first, third, and so on.
For Example:
- Pratiksha achieved the second position in the class.
- Mango was the third fruit I ate on the picnic.
- They destructed a third building in my society.
- I observed the fifth book lying on the table.
- Riya posted her eighth video today.
ii) Indefinite Numeral Adjectives
- The indefinite numeral adjective shows the quantity or amount of an uncountable noun.
- It does not represent specific numbers.
- For Example – many, some, few, any, most, more, much, enough, too much, too many, etc.
For Example:
- We spotted a few mistakes in the research paper.
- I cannot drink more milk now.
- We didn’t spend too much money on shopping.
- There isn’t enough clay left for modelling.
- Jinisha was having too much pain in her throat.
iii) Distributive Numeral Adjectives
- Distributive numeral adjectives showcase the individuality of a noun but in a cluster form by using words such as each, every, either, neither, any, none, one, everyone, and anyone.
- Here, the noun is countable.
- Noun or pronoun should be placed later than a distributive numeral adjective.
For Example:
- Every student will go to the picnic.
- Each kid will get a chance to win a football in a gaming competition.
- Any person can learn at any age.
- I am giving both dresses to my sister.
- They fit neither chair in this office space.
Compound adjective
- A compound adjective is the combination of two or more words used to create a new adjective.
- A hyphen (-) should be used to create a compound adjective. The whole meaning of words will change if we do not use a hyphen in the middle of words.
For Example:
- P.V. Sindhu is a well-known sportsperson in the Badminton field.
- Riya opts for a short-term computer course.
- We packed ready-made food for camping.
- She wrote a ten-page article on “Cleanliness”.
Collocation of adjective
- Collocation of adjectives is the group of words that we commonly used together as a habit in our daily lives.
- There is no usage of hyphens between them.
- The rule of creating collocation of adjectives is: Adjective + Noun
For Example:
- There was a heavy fall in health insurance this year.
- Manvi wins the vocabulary competition due to her rich vocabulary.
- Trains were derailed in the heavy rainfall.
- Kiara is planning a big surprise for his sister on her birthday.
- We are decorating our house with a huge chunk of fabric.
Degrees of Comparison
Degrees of Comparison are divided into 3 parts:
Positive degree
The positive degree tells us about the attributes of a single noun, whether it is a living thing or a non-living thing.
For Example:
- Riya has a big wardrobe.
- I have prepared a small meal for my family.
- I didn’t wash the dirty clothes.
- He has made a quick decision.
- My niece gets an old car.
Comparative degree
- Comparative degree shows the adjectives or attributes by comparing only two nouns, whether a living being or a non-living being.
- In the comparative degree, we always use “than” for showing comparison.
- The adjective should be placed just before “than”.
- In addition to this, we have to add “er” to adjectives while doing comparisons between things or persons.
For Example:
- Rahul plays football faster than Aryan.
- The voice of Daksh is sweeter than Pratiksha.
- My dog is fiercer than my friend’s dog.
- My paternal grandfather is older than my maternal grandfather.
- My mobile is quicker than Alisha’s.
- My niece snores louder than my mother.
- In a few cases, “more” is used instead of “er”.
For Example:
- Ananya’s painting is more beautiful than Himanshi’s.
- Priyali is more spontaneous than Rishabh.
- My research paper is more interesting than yours.
- His car is more spacious than his sister’s.
- The elephant has more strength than the tiger.
Superlative degree
- Superlative degrees are the adjectives used for comparison among three or more than three.
- It is used to showcase the best among all.
For Example:
- I decorated the biggest cake for my friend’s birthday.
- This is the loveliest show I watch on this channel.
- I saw the fanciest lamp in an exhibition.
- My brother’s laptop is the fastest in this brand.
- Vimal’s typing is the quickest in the class.
In a few cases, “most” is used instead of “est”.
For Example:
- Aisha solved the most difficult question in this textbook.
- I have painted the most beautiful graffiti on the wall.
- She has the most wonderful cat in this society.
- He has the most extensive lawn in the house.
- You have purchased the most expensive watch of this edition.
Adjectives Practice Exercise
| 1. Which degree is used for the comparison of more than three people or objects? a) Positive degree b) Comparative degree c) Superlative degree |
| 2. What does 3W stand for the interrogative adjective? a) What, Whom, Why b) What, Which, Whose c) Whose, Whom, Why |
| 3. Fill in the blank with a suitable degree of adjective: She has ____________________ writing in our class. a) more beautiful b) most beautiful c) than beautiful |
| 4. Correct the following sentence: The designation of Tina is highest than Rishi. |
ENGLISH-RELATED CONCEPTS: